Low-cost, Low-energy Absorption with Porous Liquids (LEAP-L)
LEAP-L technology offers a cost-effective, energy-efficient, and sustainable solution for gas capture and separation via the use of environmentally friendly materials
The reliance on energy sources like biogases, natural gas, and fossil fuels in industrial processes has increased the release of contaminants into the atmosphere. Contaminants can contribute to long-term environmental challenges such as deteriorating air quality, changes in atmospheric composition, and acid rain. There is an urgent need for energy-efficient and cost-effective technologies for gas capture and separation.
Industries face increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices for gas capture and separation, which involve removing unwanted gases from emissions. Today, most methods of gas removal use amine and hydroxide solutions, which are pollutants, corrosive, toxic, and expensive. These methods also require substantial energy for material regeneration, making them less desirable. There is a growing demand for innovative, cost-effective solutions that efficiently capture contaminants while minimizing environmental impact, costs, and energy consumption.
Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories have developed Low-cost, Low-energy Absorption with Porous Liquids (LEAP-L) technology which captures carbon dioxide using a novel porous liquid made from a 2D metal-organic framework called ZIF-L and the organic solvent 2′-hydroxyactephoneone
(2HAP). It achieves selective gas capture through physisorption mechanisms, including formation of hydrogen bonds or dispersion interactions, allowing for low energy consumption. The ZIF-L and 2HAP interface provides high CO2/N2 selectivity for capturing CO2 from dilute conditions. These materials can also be regenerated using low-energy methods such as sonication, isostatic pressure, and low-temperature heating to release the captured gases and restore the materials for repeated use. This liquid-based approach allows LEAP-L to integrate easily into existing gas capture systems as a potential drop-in replacement for traditional solutions that use amine or hydroxide, reducing capital expenditures.
LEAP-L technology offers a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for gas capture and separation, with operational costs expected to be significantly lower than traditional methods. Current solutions, based on amine and hydroxide, are toxic to the environment. LEAP-L uses inexpensive and environmentally friendly materials like ZIF-L (metal-organic framework) and 2HAP (organic solvent). Current technologies require high energy for regeneration, while LEAP-L employs physisorption mechanisms that allow for less energy-intensive regeneration. This liquid-based approach may serve as a drop-in replacement for existing systems, incurring few additional costs. The estimated capture cost using LEAP-L is $80 to $85 per tonne of CO2, which can decrease to $56 to $60 per tonne with a drop-in replacement. Compared to the current cost of carbon capture, which ranges from $200 to $600 per tonne, LEAP-L offers a clear financial advantage.
- Cost Effective: It uses inexpensive and tunable starting materials to reduce costs.
- Energy Efficient: LEAP-L minimizes energy consumption with physisorption and low-energy regeneration methods, compared to traditional approaches.
- Operationally Effective: It achieves exceptional CO2/N2 selectivity and adsorption capacity, enhancing carbon capture efficiency.
- Compatible: The technology Integrates easily into current gas capture systems, eliminating substantial capital expenditures.
- Sustainable: LEAP-L is composed of non-corrosive and environmentally friendly materials, offering a sustainable solution for gas separation.
- Energy Production
- Waste Management
- Chemical Manufacturing
- Environmental Services
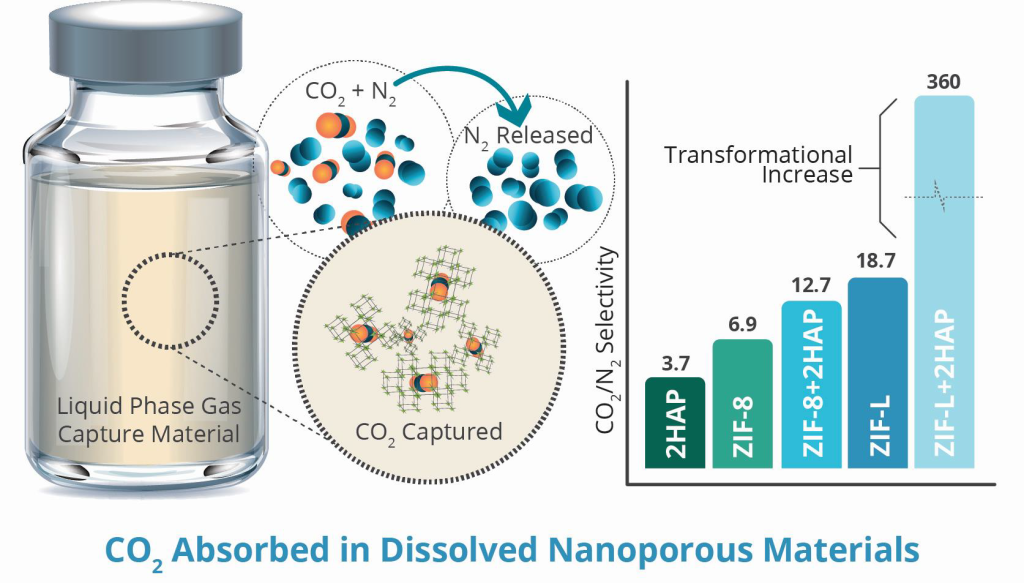
Process for achieving high CO2/N2 selectivity through liquid phase gas capture.
SD# 16680
Published8/12/2025
