Brain-Targeting Nanobodies
Nanobodies capable of penetrating the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) can act as
effective shuttles to convey chemical and biological therapeutics with targeted
specificity to the central nervous system (CNS).
The biomedical community has long struggled with the development and delivery of safe and effective chemical/biological therapeutics across the blood brain barrier. The primary obstacle of which, is finding a shuttle capable of traversing the intact Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB), which inherently restricts the passive and selective transport of ions, molecules, cells, and pathogenic agents into the brain. The absence of an effective transport mechanism capable of rapidly reaching the brain parenchyma without disrupting the blood-brain barrier (BBB) has hindered advancements in the effective treatment of a variety of disorders affecting the central nervous system (CNS). Current therapeutic delivery methods predominantly rely on receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) imparted by a limited number of ligands with suboptimal transport efficiency, leading to a plateau in advancing BBB penetrating (BBBP) drugs over the last 15 years.
Current targets (e.g. insulin and transferring receptors) for RMT lack robust tissue specificity leading to off-target effects and show limited efficacy in vivo, with a BBBP delivery rate of ~0.1%. This has led to a significant unmet need for an effective delivery method that can penetrate the BBB and shuttle therapeutics or diagnostic agents into the brain at physiologically relevant levels rapidly, with high tissue specificity, leading to less material per dose, which improves pharmaceutical companies’ ability to produce the quantities needed for distribution.
Sandia’s nanobody constructs which are strategically engineered to penetrate the BBB, provide a transformational solution to this challenge. Our technologies can therefore serve as efficient shuttles for the delivery of a variety of therapeutic and diagnostic agents, paving the way to address myriad neuropathological diseases and disorders.
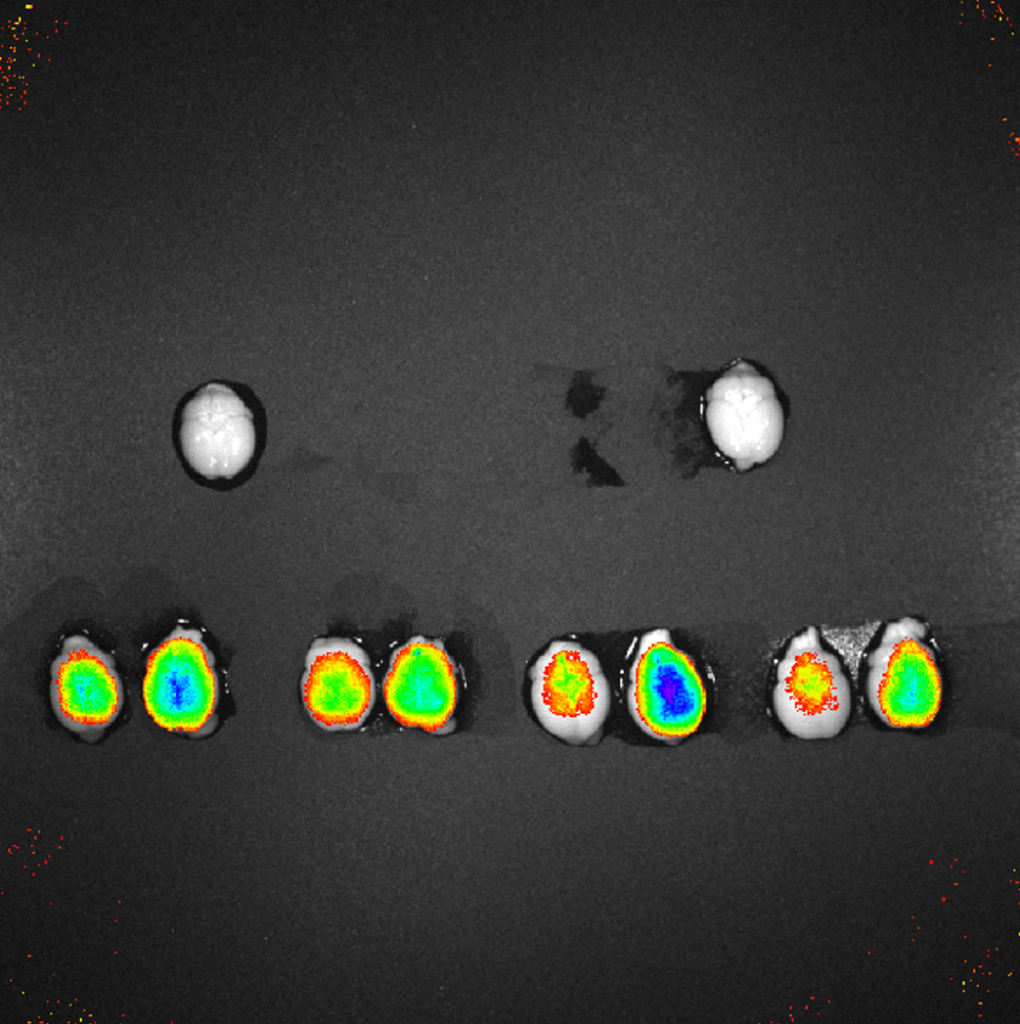
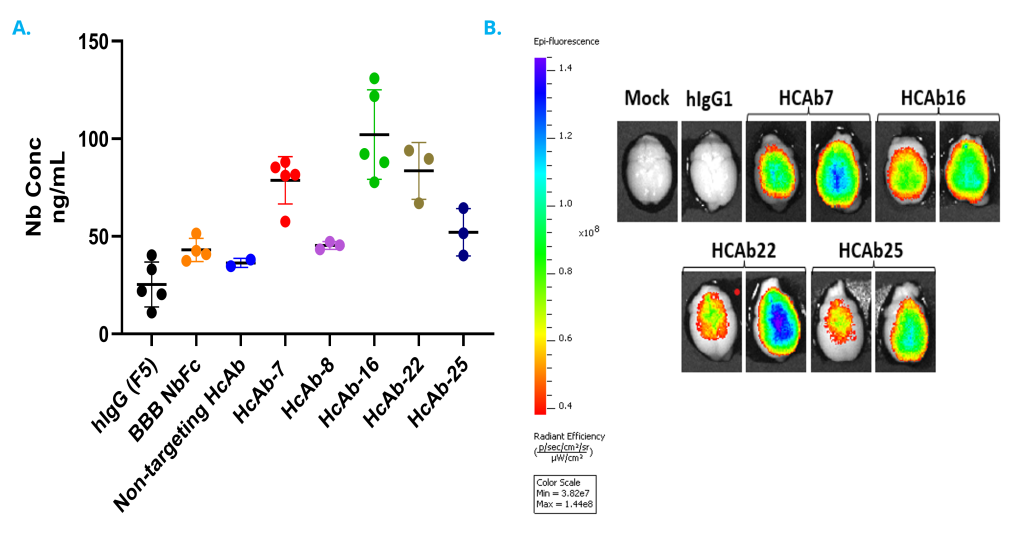
Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories have leveraged the modularity of these BBB-targeting nanobodies (Nbs) to engineer heavy chain only antibodies (HCAbs) that retain the BBB penetration kinetics of the Nb, as well as brain-targeting, antiviral bispecific assembly constructs (bsHCAbs) that are rapidly delivered to the brain and remain detectable for several days post administration. These technologies can also be applied to conjugation with a nanoparticle containing a drug payload or directly with a small molecule (e.g. Antibody-drug-conjugates) for rapid, specific delivery.
These technologies offer numerous avenues for exciting pharmaceutical applications, potentially broadening the prophylactic and therapeutic windows for the treatment of malignancies, infections, and degenerative disorders of the central nervous system. They also provide an opportunity to advance neurological diagnostic measures and research within the fields of neurobiology, neuroimmunology, and bioengineering. The modularity and versatility of these technologies makes them highly relevant to academic and private research institutions, the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry, the biomedical diagnostics sector, and government agencies.
Next Steps
- Nanobody constructs capable of penetrating the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) in Nb, HCAb, or bsHCAb format.
- Effective shuttles for the delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic agents to the central nervous system (CNS).
- Four to ten-fold enhanced delivery of brain-targeting therapeutic and diagnostic agents compared to current solutions, which possess a brain delivery rate of ~0.1%.
- Biotechnology and Medical Device
- Neurobiology
- Cancer biology
- Pharmaceutical
- Medical diagnostic
- Academic and private research institutions
- Government agencies
SD# 15931
Published5/19/2025
Last Updated5/19/2025
